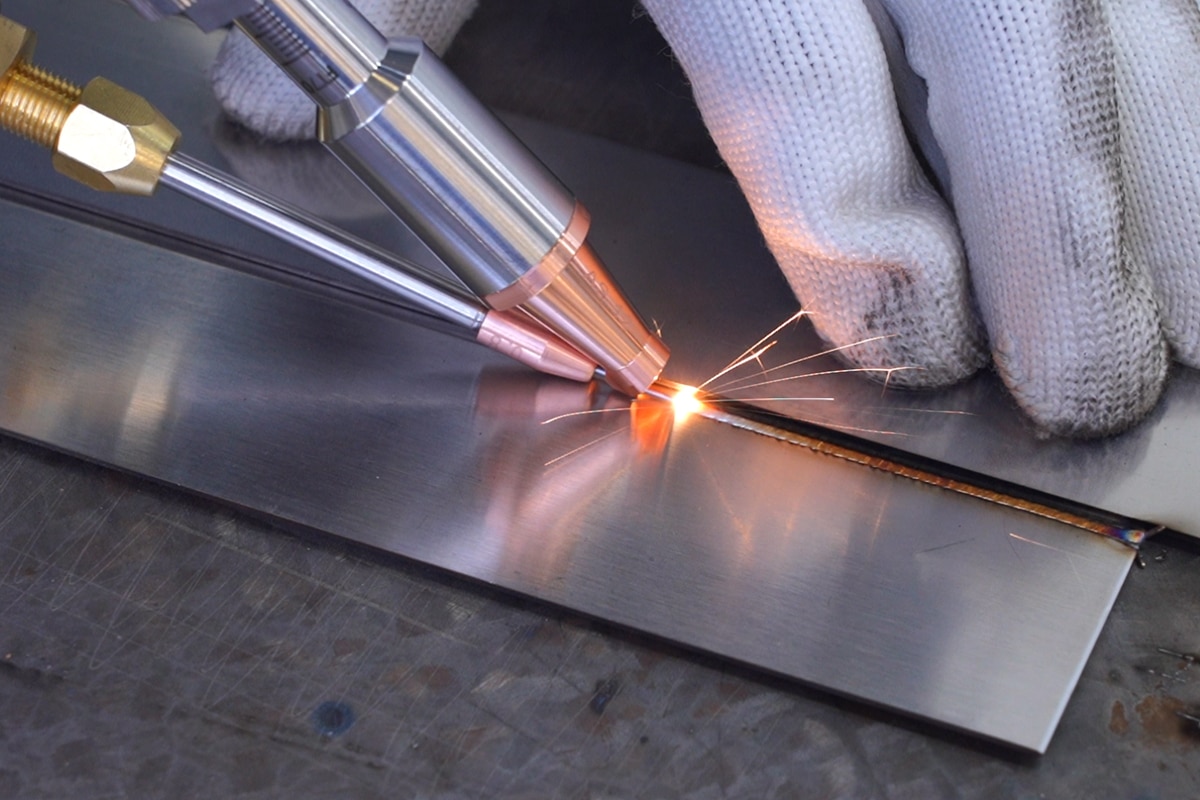
Introduction
Automatic Laser Welding Machines
-
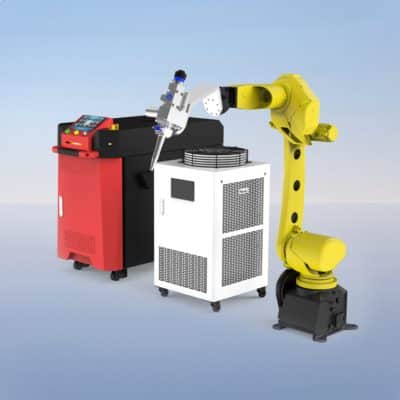

VIW-R Laser Welding Machine
Rated 4.50 out of 5$18,800.00 – $23,400.00Price range: $18,800.00 through $23,400.00 Select options This product has multiple variants. The options may be chosen on the product page
Applications







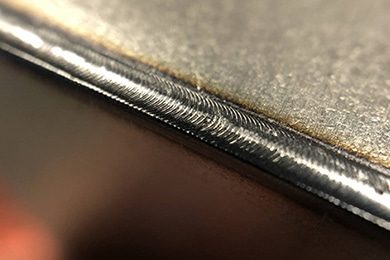
Advantages of Automatic Laser Welding
High Precision
Laser welding ensures exceptional accuracy, making it ideal for intricate designs and micro-welding applications. The concentrated laser beam provides fine control, resulting in minimal distortion and high-quality welds, even on delicate materials.
Faster Welding Speed
With its rapid welding process, the automatic laser welding machine significantly reduces cycle times, enhancing productivity. This speed advantage makes it ideal for high-volume production environments, allowing manufacturers to meet demanding output requirements efficiently.
Minimal Heat-Affected Zone
The precision of laser welding minimizes the heat-affected zone (HAZ), reducing the risk of warping, distortion, or thermal damage to surrounding materials. This ensures high-quality welds with better structural integrity and fewer post-welding processes.
Automation and Consistency
Automatic laser welding machines are highly automated, ensuring consistent weld quality with minimal human intervention. This reduces the likelihood of errors, maintains uniformity in production, and improves the overall reliability of manufacturing processes.
Versatility with Materials
Laser welding machines can process a wide range of materials, including metals, alloys, and even some plastics. Their versatility makes them suitable for various industries, from automotive to electronics, offering flexible solutions for diverse applications.
Cost-Effective in the Long Run
Although the initial investment may be higher, the efficiency, reduced labor costs, and minimal material waste delivered by automatic laser welding machines lead to long-term savings, making them a cost-effective choice for manufacturers seeking high-quality, sustainable production.
Comparison with Other Welding Methods
| Feature | Automatic Laser Welding | TIG Welding | MIG Welding | Plasma Arc Welding |
| Weld Quality | High precision, minimal heat distortion | High-quality welds, slower speed | Good quality, but prone to spatter | Very high quality, minimal spatter |
| Welding Speed | Very fast, ideal for high-volume production | Slow, manual process | Faster than TIG, but less precise | Fast, but complex setup and maintenance |
| Heat-Affected Zone (HAZ) | Minimal, reducing risk of warping and distortion | Large, leading to potential material changes | Larger HAZ, especially on thicker materials | Minimal, with controlled heat input |
| Material Versatility | Can weld a wide range of materials, including thin and complex geometries | Best for thin metals like stainless steel and aluminum | Works well with ferrous and non-ferrous metals | Suitable for a variety of metals, but limited by cost |
| Automation Capability | Fully automated, reducing human error and enhancing consistency | Requires skilled operator, limited automation | Some degree of automation, less consistent | Moderate automation, but operator skill needed |
| Ease of Use | User-friendly, minimal operator training required | Requires skilled and experienced operator | Easier to learn, suitable for medium-scale production | Requires significant operator training and expertise |
| Initial Investment | High initial cost, but low operating costs in the long term | Lower initial cost, but high labor costs | Moderate investment, with consumables costs | High initial investment, high operational costs |
| Operating Cost | Low due to minimal consumables and energy usage | Moderate, with more frequent electrode replacement | Higher due to consumables and gas usage | High due to consumables and energy consumption |
| Ideal Applications | Precision welding in industries like automotive, electronics, and aerospace | Thin materials, fine welding, and high-quality finishes | General manufacturing, heavy-duty welding | Aerospace, precision manufacturing, thin sheet metals |
Customer Reviews
Frequently Asked Questions
What Are Automatic Laser Welding Machines?
How Do Automatic Laser Welding Machines Work?
- Laser Generation: The machine generates a laser beam using a laser source, such as a fiber laser, tailored to the specific application. The beam has a high energy density, which allows it to melt materials with exceptional precision at the joint.
- Beam Delivery: The laser beam is directed to the welding area through optics like mirrors or fiber optics. The beam is then focused onto a small spot on the material using a lens, which defines the exact point where the welding takes place.
- Material Preparation: The materials to be welded are precisely positioned, either manually or automatically, under the laser beam. The automation system controls the movement of the laser or the workpiece to ensure perfect alignment and the desired weld location.
- Welding Process: The laser beam moves along the joint of the materials, heating and melting the edges as it goes. The molten material then solidifies, bonding the materials together. The machine can be programmed to follow specific welding patterns or paths based on the project’s requirements.
- Cooling: After the welding process, the molten material cools and solidifies, forming a durable bond. In certain cases, additional cooling systems are used to regulate temperature and prevent material distortion due to excessive heat.
- Quality Control: Many automatic laser welding machines come equipped with advanced sensors and monitoring systems to ensure consistent weld quality. These systems can detect deviations in real time and automatically adjust the process or alert operators if needed.
What Is the Price of Automatic Laser Welding Machines?
- Entry-Level Machines: Basic automatic laser welding machines, suitable for smaller-scale applications or less complex tasks, typically range from $20,000 to $50,000. These machines are ideal for businesses with limited production needs or for specific, straightforward welding operations.
- Mid-Range Machines: More advanced machines, offering higher power output, enhanced precision, and improved automation capabilities, generally fall between $50,000 and $100,000. These machines are designed for medium-sized operations that require consistent performance and versatility.
- High-End Machines: Industrial-grade automatic laser welding machines, featuring top-tier automation, power, and versatility, are designed for large-scale production and specialized applications. These machines typically range from $100,000 to $500,000 or more, with prices varying depending on the complexity and customization of the system.
How Accurate Are Automatic Laser Welding Machines?
- Focused Laser Beam: The laser beam is extremely focused, allowing for precise control over the welding area. This high-energy density ensures that the heat is applied only where needed, minimizing distortion and enhancing the quality of the weld.
- Advanced Control Systems: These machines are equipped with sophisticated automated control systems that precisely guide both the laser and the workpiece. The systems minimize any deviation from the desired weld path, ensuring that each weld is executed with high precision.
- Real-Time Monitoring and Adjustment: Many automatic laser welding machines feature real-time monitoring systems that continuously check the welding parameters and make adjustments as needed. This helps correct any discrepancies during the process, ensuring that the weld remains accurate throughout the operation.
- Consistent Parameters: Automation guarantees that welding parameters such as speed, power, and focus are consistent across all welds. This consistency results in uniform, high-quality welds, even during high-volume production runs.
What Is The Difference Between Handheld and Automatic Laser Welding Machines?
- Operation and Control
- Handheld Laser Welding Machines: These machines require manual operation, with the operator holding and guiding the welding head. The operator directly controls the weld path, speed, and parameters, which makes handheld systems more adaptable for small-scale or intricate tasks that need flexibility.
- Automatic Laser Welding Machines: These machines operate autonomously, following pre-programmed software. The machine automatically controls the welding path, adjusts parameters, and completes the weld without requiring continuous manual intervention. This makes them ideal for high-volume, precision-demanding, and repetitive tasks.
- Applications
- Handheld Machines: Best for smaller projects, repairs, or when working with parts that are difficult to move. They are ideal for custom, intricate welding tasks often found in maintenance, repair, or artistic applications.
- Automatic Machines: Suited for large-scale production environments, such as automotive, aerospace, and electronics industries. These machines are optimized for tasks where speed, consistency, and precision are paramount.
- Precision and Consistency
- Handheld Machines: Accuracy depends on the operator’s skill, which can result in variability in the weld quality.
- Automatic Machines: Provide highly consistent and precise welds with minimal variation, thanks to automated control systems that adjust parameters in real time.
- Cost
- Handheld Machines: Generally more affordable than automatic systems, making them accessible to smaller businesses or for specific, less complex tasks.
- Automatic Machines: Typically more expensive due to their advanced technology, automation features, and suitability for high-volume industrial applications.
How Do Automatic Laser Welding Machines Ensure Consistent Welding Quality?
- Automated Control Systems: These machines are equipped with sophisticated control systems that precisely manage key welding parameters, such as laser power, speed, focus position, and beam path. These parameters are pre-programmed and applied consistently across all welds, reducing variability that can arise with manual welding.
- Precision Laser Technology: The laser beam is highly focused, allowing for accurate and controlled energy delivery to the welding area. This precision ensures that each weld is formed under identical conditions, maintaining uniform quality in every weld.
- Real-Time Monitoring and Feedback: Many automatic laser welding machines feature sensors and cameras that continuously monitor the welding process. These systems can detect any deviations, such as changes in temperature, alignment, or material properties, and automatically adjust machine settings to correct them. This feedback loop ensures that each weld consistently meets quality standards.
- Consistent Welding Parameters: Once optimal parameters are programmed, they are applied consistently throughout the entire welding process. This eliminates the potential for human error, ensuring that each weld is made under the same conditions, resulting in high repeatability and quality.
- Environmental Control: These machines often operate in controlled environments where factors like temperature, humidity, and contamination are regulated. This minimizes external variables, ensuring the weld quality remains consistent regardless of changing external conditions.
- Advanced Motion Systems: Automatic laser welding machines utilize precise motion systems that ensure the laser follows an exact path for each weld. This level of control helps maintain consistency in the weld’s location, shape, and depth, further enhancing weld quality.
- Quality Control Integration: Some machines include integrated quality control systems that automatically inspect welds as they are produced. This immediate feedback allows for the quick detection of defects or inconsistencies, ensuring only high-quality welds are made.
What Is The Service Life of Automatic Laser Welding Machines?
- Quality of Components: High-quality machines made with durable components, such as advanced optics, reliable control systems, and robust laser sources, generally have a longer lifespan. The materials used in the construction of the machine play a crucial role in its longevity.
- Operating Environment: Machines used in clean, stable environments with controlled temperatures and minimal exposure to dust or contaminants tend to last longer. Harsh conditions, such as excessive heat, moisture, or pollutants, can cause faster wear and tear.
- Maintenance Practices: Regular maintenance, such as cleaning, calibration, and replacing worn parts, is essential for extending the service life of the machine. Failure to maintain the machine can lead to premature breakdowns and a shorter lifespan.
- Usage Intensity: Machines used continuously in high-volume production environments are more likely to experience wear compared to those used less frequently or in lighter applications. The intensity and frequency of use directly affect the machine’s longevity.
- Laser Source Life: The laser source, particularly fiber lasers commonly used in welding, has a typical lifespan of 50,000 to 100,000 hours. The quality and type of laser source directly contribute to the overall service life of the machine.
- Technological Advancements: While newer technologies may render older machines less efficient or competitive, with proper upgrades and retrofitting, many machines can continue to operate effectively beyond their expected service life.
- Manufacturer Support: Strong after-sales support, including spare parts availability and software updates, can significantly enhance a machine’s lifespan. Machines from reputable manufacturers with comprehensive customer service tend to last longer.
How To Maintain Automatic Laser Welding Machines?
- Regular Cleaning
- Optics and Lenses: Clean the laser optics and lenses regularly to remove dust, debris, or splatter that could affect the laser beam’s focus. Use proper cleaning solutions and lint-free cloths to avoid scratching these components.
- Cooling System: Ensure the cooling system is functioning properly. Regularly inspect and replace coolant fluids to prevent overheating and ensure efficient heat dissipation.
- Inspection and Calibration
- Alignment Check: Periodically check the laser beam alignment to ensure it remains focused on the weld joint. Misalignment can compromise weld quality and efficiency.
- Calibration: Calibrate the machine’s control systems and sensors regularly to maintain accuracy. This helps the machine operate within optimal parameters for precision welding.
- Lubrication
- Moving Parts: Lubricate moving components such as guide rails, bearings, and linear drives according to manufacturer recommendations. Proper lubrication reduces wear and ensures smooth operation.
- Mechanical Components: Lubricate gears, motors, and other mechanical parts regularly to prevent friction, wear, and premature failure.
- Monitoring and Diagnostics
- Real-Time Monitoring: Use the machine’s monitoring systems to track key performance metrics like power output, temperature, and welding speed. Address any anomalies promptly to prevent larger issues.
- Error Logs: Regularly review the error logs and diagnostics reports to identify potential problems before they escalate.
- Preventive Maintenance Schedule
- Routine Inspections: Establish a preventive maintenance schedule for routine checks on vital components like the laser source, optics, cooling system, and electrical connections.
- Component Replacement: Replace worn-out parts proactively—such as filters, seals, and cables—to avoid unexpected downtime and costly repairs.
- Cooling System Maintenance
- Fluid Levels: Regularly check coolant fluid levels and top them up as necessary. Ensure the coolant is free of contaminants and replace it according to the manufacturer’s guidelines.
- Cooling Unit: Inspect and clean cooling units, including radiators and fans, to maintain efficient heat dissipation.
- Software Updates
- Firmware and Software: Keep the machine’s firmware and software updated. Manufacturers often release updates to enhance performance, address bugs, and improve security.
- Backup Settings: Regularly back up settings and configurations to prevent data loss in case of a system failure.
- Training and Documentation
- Operator Training: Ensure operators are well-trained in proper machine use and maintenance practices. Proper handling can significantly reduce wear and tear.
- Maintenance Log: Keep a detailed log of all maintenance activities, including inspections, calibrations, and parts replacements. This helps track machine performance over time.
- Environmental Control
- Operating Environment: Keep the machine in a clean, controlled environment to minimize exposure to dust, humidity, and temperature fluctuations. This reduces the risk of damage to sensitive components.
- Manufacturer Support
- Technical Support: Reach out to the manufacturer’s technical support for complex maintenance issues. Regular consultations can help identify potential problems early and prevent major disruptions.
Related Resources
2026 Best CO2 Laser Cutter for Small Business
Laser Marking VS Screen Printing
Laser Welding VS MIG Welding
Laser Rust Removal VS Sandblasting Rust Removal
Contact Us
Contact Information Form:




