Introduction
Fiber Laser Marking Machines
-
VIM-FD Laser Marking Machine
Rated 4.75 out of 5$2,000.00 – $20,000.00Price range: $2,000.00 through $20,000.00 Select options This product has multiple variants. The options may be chosen on the product page -
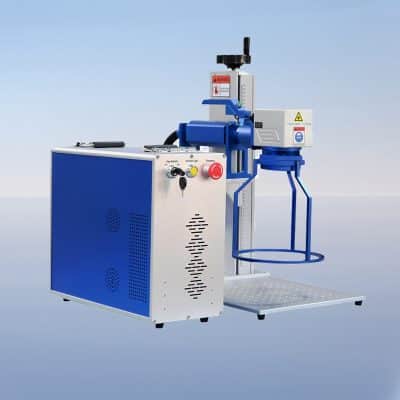

VIM-FH Laser Marking Machine
Rated 4.75 out of 5$2,200.00 – $20,200.00Price range: $2,200.00 through $20,200.00 Select options This product has multiple variants. The options may be chosen on the product page -

VIM-FS Laser Marking Machine
Rated 4.50 out of 5$2,300.00 – $20,300.00Price range: $2,300.00 through $20,300.00 Select options This product has multiple variants. The options may be chosen on the product page -

VIM-FP Laser Marking Machine
Rated 5.00 out of 5$2,100.00 – $20,100.00Price range: $2,100.00 through $20,100.00 Select options This product has multiple variants. The options may be chosen on the product page -

VIM-FE Laser Marking Machine
Rated 4.75 out of 5$2,750.00 – $20,750.00Price range: $2,750.00 through $20,750.00 Select options This product has multiple variants. The options may be chosen on the product page -

VIM-FF Laser Marking Machine
Rated 4.50 out of 5$3,500.00 – $21,500.00Price range: $3,500.00 through $21,500.00 Select options This product has multiple variants. The options may be chosen on the product page
Applications








Advantages of Fiber Laser Marking
Exceptional Precision
Fiber laser marking offers remarkable accuracy, allowing for fine and intricate details to be etched or engraved with clarity on a variety of materials, ensuring high-quality and professional results every time.
Durability and Permanence
The marks created by fiber laser technology are permanent, and resistant to fading, abrasion, and corrosion. This ensures that markings remain legible and intact throughout the lifespan of the product, even in harsh environments.
Fast and Efficient
Fiber laser marking machines operate at high speeds, dramatically increasing production efficiency while maintaining precision. This makes them ideal for industries requiring quick turnaround times and high-volume production.
Low Operating Costs
With no consumables needed, fiber laser marking machines require minimal maintenance. The absence of inks or chemicals reduces operational costs, making them a cost-effective solution for both small and large production runs.
Versatile Material Compatibility
These machines can mark a wide range of materials, including metals, plastics, ceramics, glass, and more, making them highly versatile and suitable for diverse applications across multiple industries.
Environmentally Friendly
Unlike traditional marking methods that rely on inks and solvents, fiber laser marking is a clean, eco-friendly process that produces minimal waste and consumes less energy, reducing its environmental footprint.
Comparison with Other Marking Methods
| Feature | Fiber Laser Marking | Dot Peen Marking | Inkjet Printing | Thermal Transfer Printing |
| Precision | High precision, ideal for small, intricate designs. | Moderate precision, suitable for basic and larger markings. | Low precision, suitable for general printing. | Moderate precision, used for labeling and barcodes. |
| Durability of Marking | Permanent, highly resistant to wear, corrosion, and fading. | Permanent, but susceptible to wear and abrasion. | Temporary, fades easily, especially on exposed surfaces. | Permanent, resistant to fading and wear. |
| Speed | Extremely fast, ideal for high-volume production. | Moderate speed, generally slower than lasers. | Very fast but can be inconsistent depending on surface. | Fast, especially for batch printing, but slower than lasers. |
| Material Compatibility | Works on metals, plastics, ceramics, glass, and more. | Primarily used on metals, especially hardened ones. | Limited to non-porous surfaces like plastic and glass. | Works on materials like paper, plastic, and coated metals. |
| Operating Costs | Very low, no consumables or chemicals needed. | Low maintenance but requires occasional tool replacement. | High costs due to frequent ink/toner replacements. | Low cost for consumables but may need ribbon replacements. |
| Environmental Impact | Eco-friendly, no chemicals or consumables used. | Minimal, uses less energy and consumables. | High environmental impact due to chemicals and inks. | Eco-friendly, minimal waste and energy consumption. |
| Maintenance | Very low, solid-state design, minimal downtime. | Moderate maintenance, occasional re-calibration needed. | Frequent maintenance required due to ink clogging and printhead issues. | Low maintenance, but requires periodic ribbon replacements. |
| Marking Types | Can mark text, logos, barcodes, QR codes, and more. | Marks simple text, logos, and serial numbers. | Primarily for printing large quantities of labels and basic designs. | Best for text and barcode printing on labels and packaging. |
| Depth of Marking | Capable of deep engraving, especially on metals. | Shallow marking, suitable for surface-level marks. | No engraving, just printing on the surface. | Shallow print, typically surface-level on labels. |
| Size and Portability | Compact and portable, easy to integrate into workflows. | Compact, portable, often handheld or bench-mounted. | Very portable, desktop and mobile versions available. | Desktop units available, portable and easy to use. |
| Initial Cost of Equipment | Moderate to high initial investment, but fast ROI. | Lower initial cost but less efficient for high-volume needs. | Low initial cost, but high ongoing consumable costs. | Low to moderate initial cost, depending on printer type. |
| Energy Consumption | Low energy consumption, highly efficient. | Low energy consumption, more energy-efficient than other methods. | Moderate energy consumption depending on printhead technology. | Low energy consumption, efficient for long runs. |
Customer Reviews
Frequently Asked Questions
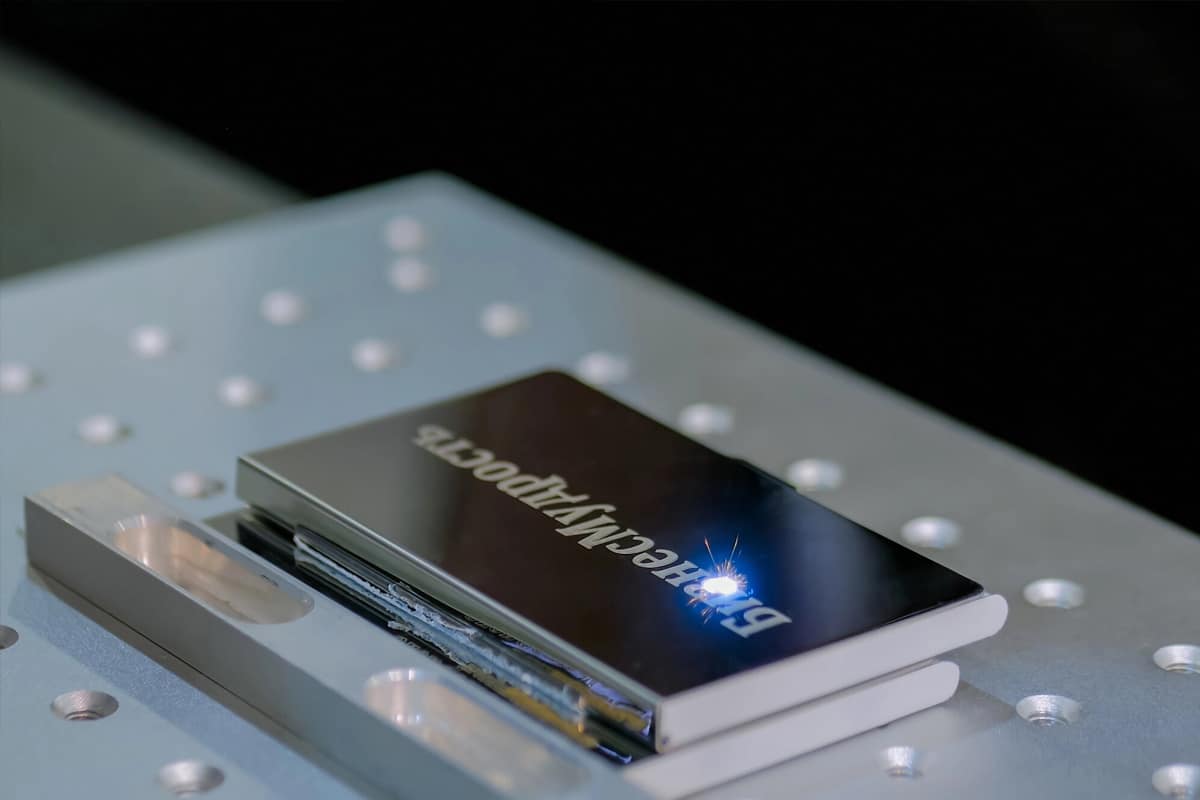
What Are Fiber Laser Marking Machines?
How Do Fiber Laser Marking Machines Work?
- Laser Generation: The heart of a fiber laser marking machine is its laser generator, which is powered by a fiber optic cable doped with rare-earth elements like ytterbium. When electrical energy is pumped into the fiber, it excites the dopant ions, producing a focused, high-intensity laser beam.
- Beam Delivery: The laser beam is transmitted through the fiber optic cable to the marking head. The fiber helps maintain the beam’s intensity and quality, ensuring it can be precisely directed onto the material with high accuracy.
- Focusing: In the marking head, the laser beam is focused using a combination of lenses and mirrors. This reduces the beam’s diameter to a microscopic level (as small as a few micrometers), enabling fine, intricate markings on the material’s surface.
- Marking Process: The focused laser beam interacts with the surface in different ways, depending on the settings and material:
- Engraving: The laser removes a small amount of material by vaporizing it, creating deep, permanent marks.
- Etching: The laser alters the material’s surface structure without removing the material, creating marks through color changes or textures.
- Annealing: The laser heats the material just below its surface, causing oxidation and creating a mark without altering the material’s structure.
- Movement Control: Fiber laser marking machines are typically equipped with computer-controlled motion systems, which precisely position the laser beam or the workpiece. This system enables the creation of complex designs, logos, barcodes, or text, ensuring consistent and accurate marking across various parts or batches.
- Cooling and Safety: To prevent overheating, the machine is equipped with a cooling system that maintains optimal performance. Additionally, safety features such as enclosures or shields protect the operator from potential exposure to the laser beam.
- Software Control: The marking process is controlled by specialized software that enables users to design patterns, input text, adjust parameters like laser power, speed, and focus, and manage the machine’s motion. This software makes it easy to customize the process for specific materials and applications.
What Are Fiber Laser Marking Machines Used For?
- Product Identification and Traceability: Fiber laser marking machines are widely used to engrave serial numbers, barcodes, QR codes, and batch numbers. This is essential for traceability in industries like automotive, aerospace, and electronics, ensuring products are easily tracked throughout their lifecycle for quality control and compliance.
- Branding and Labeling: These machines are ideal for engraving logos, brand names, and other identifiers on products. This is crucial in sectors like jewelry, consumer electronics, and luxury goods, where brand recognition and visual appeal are key to market success.
- Part Marking in Manufacturing: In manufacturing, fiber lasers mark parts with vital information, such as part numbers, manufacturing dates, and technical specifications. These markings help with assembly, maintenance, and inventory management, ensuring parts are properly identified throughout their lifecycle.
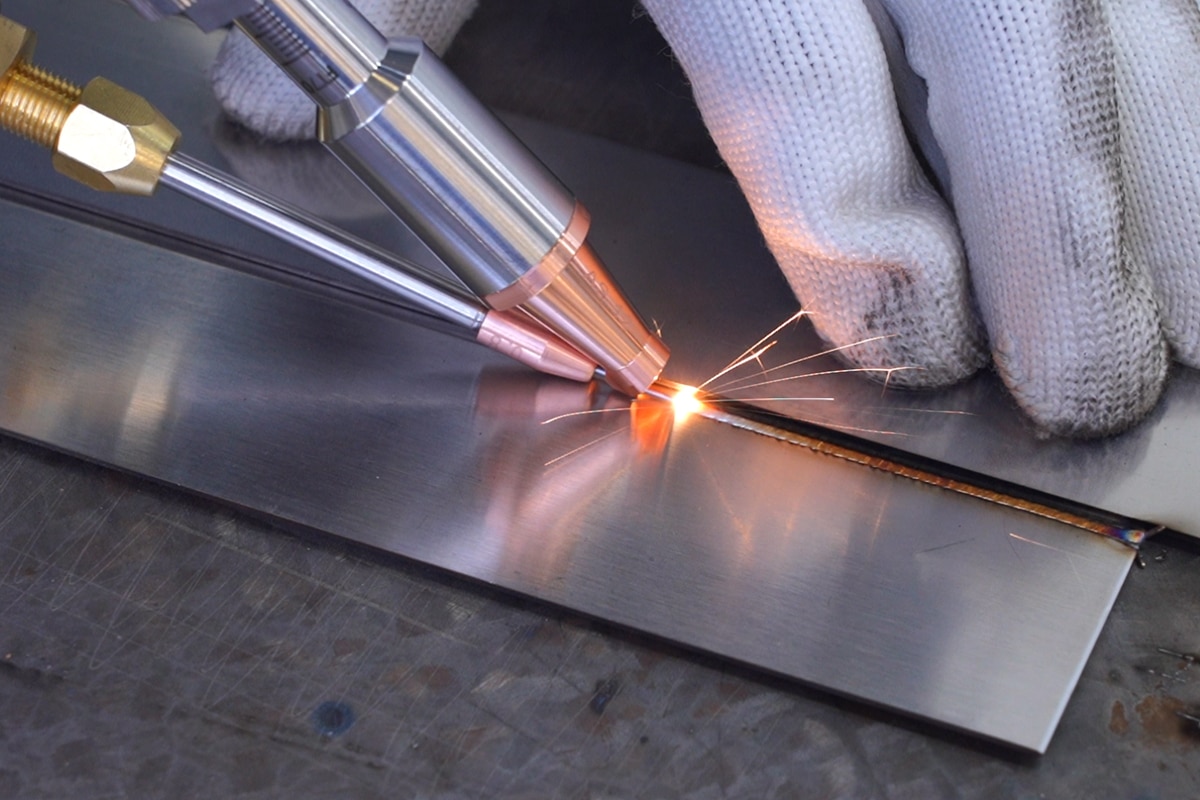
- Engraving on Metal Products: Fiber laser marking machines excel in engraving metals like stainless steel, aluminum, and titanium. This makes them invaluable for industries such as automotive, aerospace, and medical devices, where high-precision, durable markings are required on metal components.
- Personalization of Products: Fiber lasers are also used to personalize products by engraving custom designs, names, or initials. Common in jewelry, watches, and gifts, this adds a unique touch to products, enhancing their appeal and value.
- Marking on Electronic Components: In the electronics industry, fiber laser marking machines engrave detailed information onto small and delicate components, including circuit boards, connectors, and microchips. The laser’s precision ensures high-quality marks without damaging the tiny, fragile parts.
How Much Does Fiber Laser Marking Machines Cost?
- 20W Fiber Laser Marking Machine: US$2,000 – US$6,500
- 30W Fiber Laser Marking Machine: US$2,500 – US$7,500
- 50W Fiber Laser Marking Machine: US$3,000 – US$12,000
- 60W Fiber Laser Marking Machine: Around US$3,500
- 70W Fiber Laser Marking Machine: Around US$4,000
- 100W Fiber Laser Marking Machine: US$5,500 – US$23,000
What Are the Disadvantages of Fiber Laser Marking Machines?
- High Initial Cost: Fiber laser marking machines, particularly those with higher power outputs, require a significant upfront investment. This high initial cost can be a barrier for small businesses or those with limited budgets.
- Limited Material Compatibility: These machines excel at marking metals and some plastics but are less effective on materials like wood, glass, or certain ceramics. For these materials, alternative laser types (e.g., CO2 lasers) may be necessary.
- Complexity in Setup and Operation: Despite user-friendly designs, fiber laser marking machines can still be complex to set up and operate, especially for users unfamiliar with laser technology. Proper training is required to maximize efficiency and avoid errors.
- Maintenance and Repairs: Although low maintenance compared to other laser types, fiber lasers still require periodic maintenance. If repairs are necessary, the costs and downtime can be significant, especially for specialized parts or technicians.
- Energy Consumption: Fiber laser marking machines, particularly those with higher power, can consume a lot of energy. This can lead to increased operational costs, especially in high-volume production environments.
- Size and Portability: Many industrial-grade fiber laser marking machines are bulky and not easy to move. This lack of portability can limit their use in smaller workspaces or for businesses needing flexibility.
- Limited Depth for Certain Applications: While fiber lasers can achieve deep engravings, there are limits, especially when working with hard or thick materials. For applications requiring extremely deep engravings, other technologies may be more appropriate.
- Safety Concerns: Like all laser equipment, fiber laser marking machines present safety risks. Without proper safety measures, high-intensity laser beams can cause burns or eye damage, requiring strict adherence to safety protocols.
- Potential for Overheating: Continuous use, especially at high power, can cause the machine to overheat. Without proper cooling systems, this heat buildup can negatively impact performance and longevity.
- Environmental Sensitivity: These machines are sensitive to environmental factors such as temperature fluctuations, dust, and humidity, which can affect marking quality. A controlled environment is necessary for optimal performance.
How Accurate Are Fiber Laser Marking Machines?
- Spot Size: Fiber lasers produce an extremely fine beam, with a spot size as small as a few micrometers (μm). This enables the creation of highly detailed and intricate designs, small text, and fine lines with minimal distortion.
- Positioning Accuracy: The positioning accuracy of fiber laser marking machines typically ranges from ±0.01 mm to ±0.03 mm, ensuring precise placement of each mark, even on complex or tiny components.
- Repeatability: These machines excel in repeatability, consistently marking the same location across multiple parts. Repeatability is often within ±0.002 mm, guaranteeing uniformity in mass production.
- Line Width: Fiber laser marking machines produce markings with extremely thin line widths, often less than 0.01 mm, allowing for fine and detailed engravings, especially for small and intricate designs.
- Depth Control: Precise control over the marking depth is one of the key advantages. Whether shallow etches or deeper engravings, fiber lasers can adjust based on material and application, ensuring accuracy in marking depth.
- Resolution: Fiber lasers boast high resolution, capable of producing complex, detailed patterns and designs, ensuring sharpness and clarity even in highly intricate markings.
- Minimal Distortion: Due to the non-contact nature of the process, fiber laser marking causes minimal material distortion. This ensures the integrity and appearance of the material remain unaltered during the marking process.
- High-Speed Accuracy: Even at high speeds, fiber laser marking machines maintain their accuracy, making them ideal for high-volume production environments without sacrificing the quality of the marks.
What Are The Operating Costs of Fiber Laser Marking Machines?
- Power Consumption: Fiber laser marking machines are energy-efficient compared to other laser types, but power consumption can still be a significant cost, especially for higher-powered machines. The typical power consumption ranges from 0.1 kW to 1 kW, depending on the machine’s power rating and usage. The cost of electricity will depend on local rates, which can range from a few cents to a few dollars per hour of operation.
- Maintenance Costs: Although fiber lasers are known for their low maintenance needs, regular upkeep is essential to ensure the machine runs smoothly. Maintenance-related costs include:
- Routine Inspections and Cleaning: Cleaning the machine and checking for wear on components helps prevent costly repairs in the future.
- Cooling System Maintenance: Machines with water cooling systems might require periodic coolant replacement and system checks, but these are generally low-cost.
- Replacement Parts: Over time, certain components like lenses, mirrors, or the laser source itself may need to be replaced. While these costs are not frequent, they can still contribute to overall operating expenses.
- Consumables: Fiber laser marking machines have relatively minimal consumable costs compared to other types of lasers. Notably, there are no gases or dyes required for operation, which significantly reduces ongoing expenses. Consumable costs may include:
- Protective Lenses: These may need replacing occasionally if they become damaged or dirty during use.
- Marking Materials: Although the laser itself doesn’t require consumables, the materials being marked (such as metals, plastics, or other substrates) are a direct cost of operation.
- Operator Costs: Operating a fiber laser marking machine typically requires a trained operator. The cost of labor will depend on the complexity of the tasks and local wage rates. However, because many fiber laser machines are automated, one operator can often manage multiple machines, which helps reduce labor costs in high-volume settings.
- Software and Licensing: Most fiber laser marking machines come with specialized software for designing and controlling the marking process. The software is typically included in the initial machine purchase, but there could be additional costs for:
- Software Updates: Some manufacturers charge for regular updates to the software.
- Licensing Fees: If the machine offers advanced features or specialized functions, there may be ongoing licensing fees.
- Downtime Costs: If the machine requires repairs or faces an unexpected breakdown, downtime can lead to lost productivity. While fiber laser marking machines are known for their reliability, unplanned downtime can still affect overall costs. Therefore, it’s important to factor in potential downtime when assessing operating costs.
- Depreciation: While not a direct operating cost, depreciation affects the long-term value of the machine. Over time, the machine’s value will decrease, which should be considered when calculating the overall cost of ownership.
What Skills Are Needed To Use Fiber Laser Marking Machines?
- Technical Knowledge
- Understanding Laser Technology: A fundamental understanding of how fiber lasers work is crucial. Operators should be familiar with concepts such as beam focus, laser power settings, and marking depth. This knowledge enables them to optimize the machine’s performance based on different materials and applications.
- Machine Operation: Familiarity with the specific model of the fiber laser marking machine is vital. Operators should know how to power the machine on and off, make adjustments to settings (such as power, speed, and focus), and operate the machine’s controls efficiently.
- Software Proficiency
- Design Software: Proficiency in design software like CorelDRAW, AutoCAD, or other specialized laser marking software is necessary for creating or importing designs. Operators must be able to format designs to meet the machine’s specifications and adjust them as needed for accurate marking.
- Machine Control Software: Operators need to understand the machine’s control software. This includes setting marking parameters, managing files, and controlling the movement of the laser head or workpiece to ensure proper alignment and execution of the design.
- Material Knowledge
- Material Properties: Operators should understand how different materials react to the laser. Knowledge of how to adjust the laser’s settings (e.g., power, speed, focus) is essential to ensure the laser marks effectively without damaging the material. For instance, metal and plastic require different laser settings for optimal results.
- Marking Techniques: Various materials require different marking techniques, such as engraving, etching, or annealing. Operators should be able to identify which technique is most suitable based on the material type and desired outcome.
- Attention to Detail
- Precision and Accuracy: Fiber laser marking machines require extremely high precision. Operators must have a sharp eye for detail to ensure the markings are placed accurately and meet the required specifications for every piece.
- Quality Control: Inspecting finished markings for quality is essential. Operators need to check for misalignments, incomplete marks, or surface damage and make adjustments as needed to maintain consistent quality.
- Problem-Solving Skills
- Troubleshooting: Operators should be capable of identifying and resolving common issues that can arise, such as inconsistent marking quality, misalignment, or software glitches. The ability to solve problems quickly is essential to minimize downtime.
- Adjusting Parameters: Being able to adjust laser settings (power, speed, frequency, and focus) allows operators to optimize the process for various materials and designs, ensuring the best possible results.
- Safety Awareness
- Laser Safety: Operators must understand the safety hazards associated with working with lasers, particularly the risks of eye and skin exposure. Proper eye protection (such as safety goggles) and adherence to safety protocols are essential to prevent accidents.
- Work Environment Safety: Awareness of general safety within the work environment is also critical. This includes proper ventilation to manage fumes generated when marking certain materials, handling hot surfaces, and ensuring the workspace is clear of hazards.
- Mechanical Aptitude
- Basic Maintenance: Operators should be able to perform basic maintenance tasks, such as cleaning lenses, replacing consumables, and ensuring the laser head is functioning properly. This routine maintenance helps prevent breakdowns and extends the life of the machine.
- Understanding Mechanical Components: Knowledge of the mechanical components of the machine—like the laser head, mirrors, and motion systems—allows operators to troubleshoot minor issues or make necessary adjustments, reducing downtime.
- Time Management
- Efficient Operation: In high-volume production settings, managing time effectively is essential. Operators should be able to quickly set up jobs, adjust parameters, and monitor progress without sacrificing the quality of the work.
- Batch Processing: For environments where multiple parts or products need to be marked, operators should have skills in managing batch processing. This ability helps maximize machine throughput while maintaining consistent quality.
Related Resources
CNC Punching Machine vs Laser Cutting: Which Is Best?
2026 Best CO2 Laser Cutter for Small Business
Laser Marking VS Screen Printing
Laser Welding VS MIG Welding
Contact Us
Contact Information Form:








